The rise of AI in tech and engineering directly impacts how organisations hire and develop talent.
Here are 6 ways how forward-thinking companies are adapting for AI implications for hiring talent:
1. Hiring for AI Proficiency
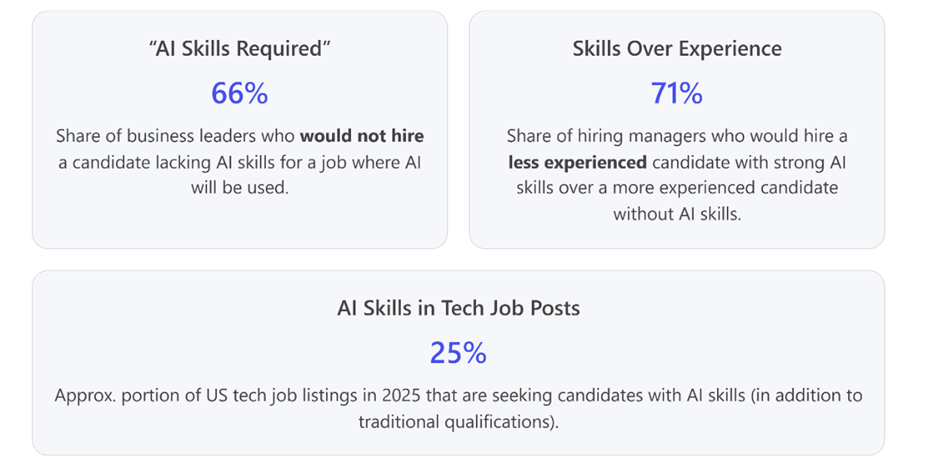
Organisations now prioritise AI skills in recruitment. Across industries, 66% of business leaders say they would not hire someone without AI skills for roles where AI is relevant. While candidates don’t need to be AI experts, they must demonstrate basic competency—just as basic computer literacy became a standard expectation.
In tech roles, AI fluency often outweighs years of experience. A 2024 survey found that 71% of hiring managers would choose a candidate with strong AI skills and less experience over a more experienced candidate lacking those skills. For example, recruiters may favour a software engineer who automates workflows using AI tools over one who relies solely on manual methods.
Frontier hiring organisations are updating interview formats to reflect this shift. Common strategies include:
Asking candidates to describe how they’ve used AI or automated tasks.
Allowing or encouraging AI use during coding tests to observe collaboration.
Designing case studies around improving processes with AI or interpreting AI outputs.
Companies also highlight their AI-enabled environments in job descriptions to attract candidates who want to work with cutting-edge tools. Conversely, firms that don’t offer modern AI tools risk losing top talent.
2. Upskilling Current Employees
Hiring isn’t the only solution—organisations are investing in reskilling their existing workforce. They offer formal training on internal AI platforms, host workshops on prompt engineering, and provide access to online AI courses.
Nearly half of business leaders (47%) say they focus on upskilling employees to thrive in human+AI workflows. However, a gap remains: while 67% of leaders understand AI agents, only 40% of employees do. Companies must bridge this divide to ensure everyone “speaks AI” to some degree.
3. Evolving Career Paths
AI is reshaping early career experiences. Entry-level engineers now take on oversight and AI coordination tasks earlier than before. This accelerates skills like system design but may slow mastery of fundamentals.
Organisations must rethink mentorship and onboarding. For example, junior engineers should review AI-generated outputs with senior colleagues to build foundational skills. Career paths may include roles like “AI Tool Specialist” or “Automation Strategist” as stepping stones.
4. Creating New Roles and Seeking Interdisciplinary Talent
New roles are emerging, such as “AI Workflow Coordinator,” “Prompt Engineer,” and “AI Ethics Lead.” Companies also seek hybrid skillsets—like a developer with a background in psychology or design—to build AI systems that interface well with humans.
Recruiters increasingly value versatile candidates who can adapt across domains. As AI handles technical execution, humans who bridge technical and non-technical areas bring added value.
5. Hiring for Culture and Retention
Recruiters must assess whether candidates embrace human-AI collaboration. Someone who resists using AI may struggle in a modern tech environment, while someone who over-relies on it without understanding its limits could pose risks.
Interviewers ask questions about how candidates stay current with tech trends and how they feel about automation. Companies also promote their culture of innovation and continuous learning to attract adaptable talent.
6. Redefining Success and Performance Metrics
AI is changing how organisations measure performance. Instead of tracking lines of code, companies assess outcomes achieved through AI collaboration.
Hiring profiles may include metrics like:
“Delivered 30% productivity improvement via automation.”
“Led an AI adoption initiative.”
CVs increasingly list AI tools alongside programming languages. Interviewers ask candidates how they’ve used AI to improve their work.
Challenges and Considerations
Despite the benefits, AI integration introduces challenges:
Maintaining Human Expertise: Over-reliance on AI can lead to knowledge gaps. Companies must balance AI use with deliberate learning—such as code reviews and training sessions focused on AI-generated outputs.
Quality Control and AI Limitations: AI can introduce errors or bias. Organisations must keep humans in the loop and invest in verification tools. Roles like “AI Auditor” or training QA engineers in AI oversight are becoming common.
Ethical and Workplace Concerns: AI may displace certain roles or introduce bias. Companies must offer reskilling programmes and build Responsible AI frameworks with clear policies and open feedback channels.
Employee Morale and Change Management: While AI can improve job satisfaction, it may also cause anxiety. Leaders must reinforce the evolving value of human roles and support employees through change management programmes.
Infrastructure and Security: Deploying AI at scale requires robust infrastructure and clear data security policies. Companies must invest in IT systems and hire talent with expertise in AI platforms and cybersecurity.
Long-Term Implications
AI will reshape the workforce. Smaller teams may achieve what larger ones did in the past. This increases competition for top talent but also opens doors for non-traditional candidates who master AI tools.
Organisations must plan strategically—identifying which skills to build internally, which roles to hire for, and how to redesign jobs for human-AI synergy.
Success will depend on:
Innovation: Are employees using freed-up time for creative work?
Agility: How quickly can teams adapt to new AI capabilities?
Engagement: Do employees feel empowered by AI?
In conclusion, the future of tech and engineering lies in human-AI collaboration. Companies must reinvent how work gets done, embedding AI into processes and reimagining roles. Job seekers must evolve too—those who embrace AI and bring higher-order thinking will become the most valuable.
Success requires more than adopting tools. It demands adaptive leadership, culture, and investment in learning.
You May Also Like
People + AI: A New Factor of Production →
Emergence of AI as a new factor of production alongside human effort.
AI Integration Into HR Systems →
Seamless AI integration with HR systems for adopting AI in hiring.
Redesigning Workflows to Integrate AI →
Learn how companies are redesigning workflows to integrate AI.
AI in Recruitment Process (Industry Report) →
Industry report on how AI tools can be used in sourcing, screening and interviewing.
7 Risks from using AI in Recruitment →
Learn critical risks from using AI in Recruitment.
