By 2025, AI agents in HR have become a growing trend. AI agents help with talent sourcing, CV screening, interview scheduling, onboarding, and even performance management.
Most HR professionals using AI report major time savings and improved efficiency. Rather than replacing HR teams , AI tools support them—handling repetitive, data-heavy tasks so people can focus on strategy and relationships.
For example, IBM’s CEO said AI freed up budget and capacity to hire more developers and sales staff, even after automating hundreds of HR roles.

Here are examples of how major companies are activating AI Agents in HR with some business value.
Amazon: Scaling Hiring with AI and Promoting Inclusivity
By 2025, Amazon has embedded AI across its high-volume hiring process. Its People eXperience and Technology (PXT) team developed tools for each stage of recruitment:
Smart Job Matching: Amazon’s careers site uses machine learning to recommend roles based on a candidate’s search and browsing behaviour—improving job fit from the start.
Automated CV Screening: For roles with many applicants, AI identifies strong candidates and fast-tracks them. Human recruiters still review all applications, but AI ensures no qualified candidate is missed. Internal analysis shows this tool boosts hiring rates without introducing bias.
Online Assessments & Virtual Interviews: Candidates complete AI-scored tests at their convenience. These standardised assessments reduce unconscious bias and help diverse talent shine—especially those from non-traditional backgrounds.
AI Recommendations for Recruiters: AI suggests alternative roles for candidates based on CV content. For example, someone mentioning “machine learning” might be considered for multiple ML roles. A dedicated team monitors these suggestions to ensure fairness.
All tools are integrated into Amazon’s internal recruiting platform. Recruiters use AI insights, but retain final decision-making authority.
Amazon’s VP of PXT Science stresses that their tech is “born inclusive”—designed from the ground up to promote equity. Before launch, each tool undergoes bias testing and user research.
This approach stems from lessons learned—like the 2018 incident where an experimental hiring algorithm showed bias against women and was scrapped. That project never went live, but it shaped Amazon’s fairness-first design philosophy.
Amazon’s AI tools have sped up hiring and improved inclusive hiring. Candidates now move from application to interview in hours, not weeks. Online assessments allow applicants to showcase skills early, and fewer are left waiting for responses. Given Amazon’s massive hiring volume, AI has been essential to scale.
Interestingly, Amazon bans candidates from using AI tools (like ChatGPT) during interviews. The company wants to assess real skills, not AI-generated answers—highlighting its commitment to authenticity.
Looking ahead, Amazon is updating its AI tools to meet new regulations (like NYC’s bias audit mandate) and expanding them globally. Amazon’s goal remains: make hiring faster and fairer using cutting-edge technology.
Google: Generative AI Copilot for Recruiters and New Hires
At Google, generative AI has transformed HR. By 2025, Google Cloud’s HR team uses an AI assistant—code-named “Gemini for Workspace”—across recruitment and onboarding.
Talent Sourcing: Recruiters input job criteria, and the AI scans millions of past applications to find top matches in minutes. This speeds up hiring and lets recruiters focus on personal outreach.
Interview Feedback Summarisation: Google’s AI summarises feedback from multiple interviewers, helping hiring committees form a balanced view of each candidate and reducing bias.
Onboarding Concierge: New hires use the AI to find documents, training modules, and career development resources. It acts as a coach, helping them settle in quickly and confidently.
Google plans to expand this AI across its HR functions—automating job descriptions, interview scheduling, and multilingual support. Crucially, humans remain in control. The AI suggests, but people decide.
The results are clear: faster hiring, better-informed managers, and smoother onboarding. Google’s high offer acceptance rates (over 90%) reflect the strong candidate experience AI helps deliver.
Meta: Piloting an AI-First Hiring System
In 2025, Meta is trialling a fully AI-driven hiring system. Key features include:
Automated Technical Screening: AI administers and scores coding tests for engineering roles.
Interview Question Suggestions: AI prompts interviewers with tailored questions based on candidate profiles.
Interviewer–Candidate Matching: AI pairs candidates with suitable interviewers based on skills, language, and availability.
Admin Automation: AI handles scheduling, reminders, and note transcription.
Interviewer Quality Control: AI monitors interviews for inappropriate questions and evaluates feedback quality.
Meta’s goal is to streamline hiring, improve consistency, and reduce bias. Humans still conduct final interviews and make hiring decisions, but AI handles much of the groundwork.
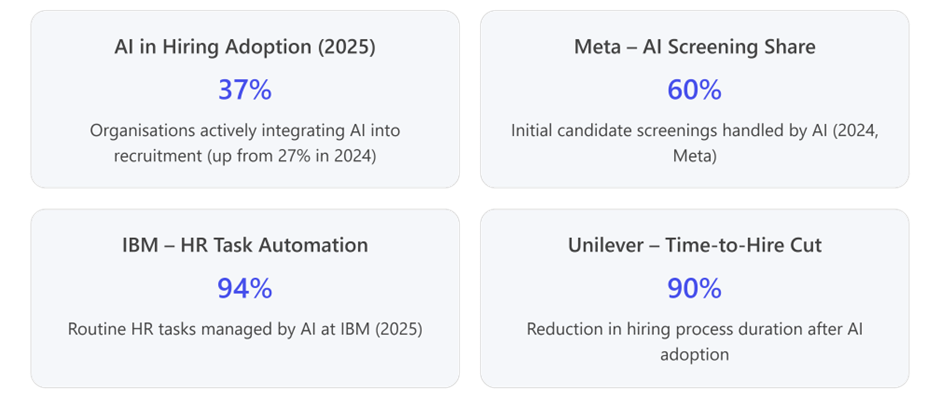
By late 2024, Meta had already automated 60% of initial screening and used predictive analytics to identify high-potential hires. These efforts cut time-to-hire by 45% and boosted recruiter efficiency by 40%.
Meta also trialled “AI-assisted interviews”, where candidates use AI tools during coding tests—reflecting real-world developer workflows. This contrasts with Amazon’s ban and sparked industry debate.
The company sees AI as a stage manager for hiring—coordinating tasks, improving communication, and enhancing fairness. Early results are promising, and Meta believes this approach will shorten hiring cycles and improve candidate experience.
IBM: Automating HR at Scale
By 2025, IBM automates 94% of routine HR tasks using AI.
Key systems include:
AskHR Chatbot: Handles over 2 million employee queries annually, now upgraded with generative AI to take actions (e.g., updating bank details).
Document Generation: AI drafts performance reviews and development plans, saving managers time and improving consistency.
Workflow Orchestration: AI compiles promotion dossiers and guides managers through performance decisions.
Predictive Analytics: AI forecasts attrition risk and matches talent to internal roles.
IBM’s AI rollout led to job reductions in HR, but the company reinvested in product and sales roles. Many HR staff were upskilled to manage AI systems or moved into strategic roles.
The company reports $3.5 billion in productivity gains, faster HR services, and improved compliance. IBM’s HR now operates as a hybrid team—AI handles processes, humans provide empathy and strategy.
Responsible AI Agents in HR
Another major trend is responsible AI use. Companies now monitor AI tools for bias and ensure they meet equal opportunity standards—often driven by new regulations. For instance, Meta’s AI hiring system flags non-inclusive interview questions and promotes consistent candidate evaluation.
Firms also focus on the candidate experience. When used well, AI speeds up communication and reduces the “quiet hole” effect where applicants hear nothing back. Transparency and human touch remain essential.
In summary, AI agents are now a core part of HR and recruitment at many top companies in 2025. These organisations show that when used wisely, AI can transform hiring—making it faster, more data-driven, and fairer.
Key wins include:
Cutting time-to-hire from months to weeks
Screening hundreds of CVs in the time it once took to read one
Improving or maintaining diversity by focusing on job-relevant criteria
Candidates often benefit too. They get quicker responses and new tools like interview coaching bots or gamified assessments.
But the leading companies also share a clear message: human oversight and ethical design are essential. The most successful examples—like Amazon’s inclusive tools, Meta’s AI for monitoring interviews, and IBM’s automated HR—keep humans in control. These systems are transparent, monitored for bias, and aligned with company values.
As IBM’s Nickle LaMoreaux said, bringing AI agents in HR isn’t like hiring a magic robot. It needs training, management, and clear purpose—just like any other capability.
The trend is clear: companies like Amazon, Google, Meta, IBM, and Unilever are building “AI-augmented HR.” Algorithms don’t replace recruiters—they support them. HR teams now design and guide smart processes instead of doing manual tasks.
With AI handling the routine work, HR professionals can focus on strategy, personal engagement, and complex people challenges—areas where human judgement matters most.
You May Also Like
AI Integration Into HR Systems →
Seamless AI integration with HR systems for adopting AI in hiring.
OpenAI Jobs Platform Overview →
Insights into OpenAI Jobs Platform for AI in hiring.
Redesigning Workflows to Integrate AI →
Learn how companies are redesigning workflows to integrate AI.
AI Implications for Hiring Talent →
The rise of AI in tech directly impacts how organisations hire and develop talent.
Eightfold AI: Talent Intelligence →
Eightfold AI delivers a comprehensive talent intelligence platform.
